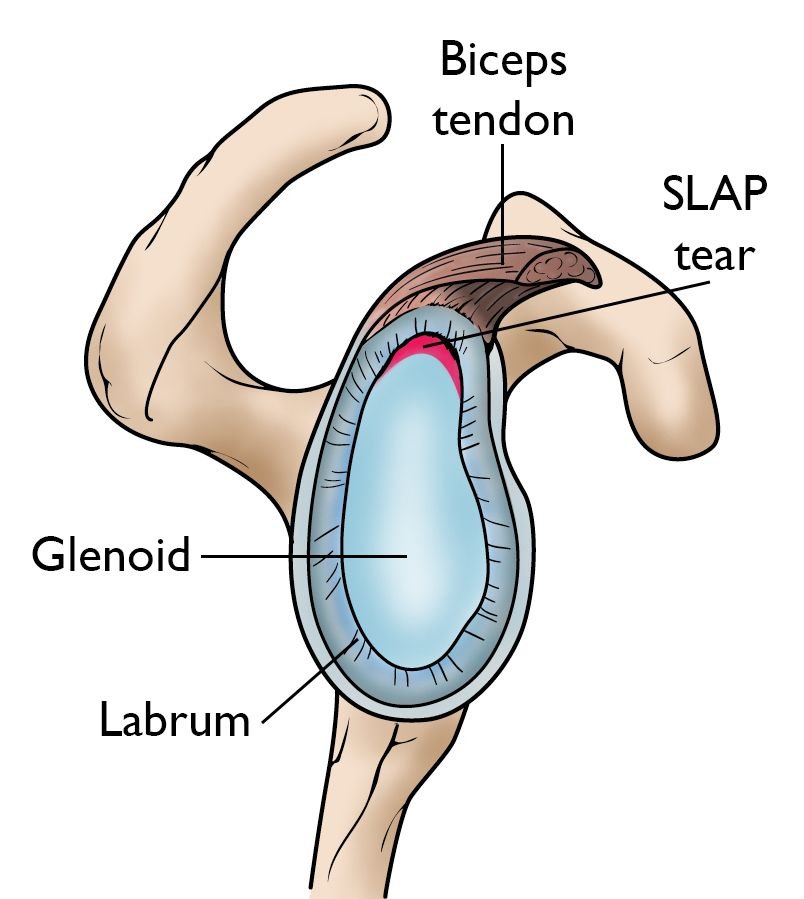
SLAP TEAR – SLAP LESION
The labrum is a thick piece of tissue that surrounds the shoulder’s socket joint. The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, but unlike your hip joint, the socket is very shallow. This allows for a larger range of motion, in fact, the range of movements your shoulder can make far exceeds any other joint in the body. The labrum helps to provide stability to this shallow socket by making the socket deeper for the ball to sit in.
When you have trauma to the shoulder, it is possible that you may have torn your labrum. The labrum becomes more brittle with age, and can therefore fray (like a rope) and tear with the aging process.
A SLAP tear is a type of labral tear most commonly seen in overhead throwing athletes such as baseball players and tennis players. The torn labrum seen in a SLAP tear is at the top of the shoulder socket where the biceps tendon attaches to the shoulder. Common symptoms of a labral tear consist of an aching sensation in the shoulder joint, a catching of the shoulder with movement, and/or pain with specific activities.
A SLAP tear or lesion is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder. The labrum is a thick piece of fibrocartilage tissue that surrounds the shoulder’s socket joint. The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, but unlike your hip joint, the socket is very shallow. The labrum makes the glenoid socket deeper and stabilizes the shoulder joint. This allows for a larger range of motion. In fact, the shoulder has the largest range of motion of any joint in the body.
Common symptoms of a labral tear consist of an aching sensation in the shoulder joint, a catching, locking or popping of the shoulder with movement, and/or pain with specific activities. The treatment of a torn labrum depends on the type of tear that has occurred. Most labral tears do not require surgery; however, in patients who have persistent symptoms despite more conservative treatments, surgery may be necessary. Non-surgical treatment include anti-inflammatory medication to reduce pain and swelling and physical therapy to restore range of motion and strengthen the shoulder. If non-surgical methods are ineffective, your doctor may recommend surgery. A common technique is shoulder arthroscopy, which relies on the insertion of a small camera to guide the surgical instruments. There are various arthroscopic procedures that can be performed on a SLAP tear, depending on your specific tear.
The treatment of a torn labrum depends on the type of tear that has occurred. Most labral tears do not require surgery; however, in patients who have persistent symptoms despite more conservative treatments, surgery may be necessary.